WHAT IS RECYCLING
Recycling means recovery & reprocessing of waste material to use in a new product. Materials which can be recycled are iron & steel scrap, aluminum cans, glass bottles, wood, plastic & paper, which serve as substitutes for raw material obtained from scarce natural resources like petroleum, natural gas, mineral ores, coal & trees.
Mainly, two types of recycling operations are internal recycling & external recycling. Internal recycling means that when the reuse in the manufacturing process of materials that are waste products of that process is done, which is common in the metal industry. External recycling means reclaiming material from a product that has been worn out or rendered useless & obsolete.
E-waste is now the fastest-growing waste stream, with computer equipment accounting for about 70% of it, followed by telecommunications (12%), electrical equipment (8%), and medical equipment (2%). (7 per cent).
E-waste, without a doubt, poses a significant environmental threat. It does, however, create enormous opportunities for entrepreneurs prepared to take the risk. According to a recent report by Assocham-Ckinetics, India is the world's fifth-largest e-waste producer, with annual e-waste creation anticipated to increase by 30% to 5.2 million metric tonnes (MT) by 2020, up from the current level of 1.8 million MT.
As a result, the e-waste recycling industry has a big revenue opportunity.
This study gives a quick rundown of the e-waste recycling industry's criteria.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), when harmful elements leached from E-Waste come into direct contact with humans, animals, or the environment, health concerns and environmental degradation can occur. Lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are examples of poisonous materials (PCBs). Inhalation of hazardous gases, as well as the accumulation of toxins in soil, water, and food, can cause serious health problems. As a result, tainted water and food will enter the human food chain, with negative consequences.
This contamination endangers not just individuals but also the environment. The risks are particularly high in developing nations because some rich countries send their e-waste for disposal. However, in light of the dangers of E-Waste, rules have been created that restrict the import and export of E-Waste. It has been discovered that worldwide e-waste has negative consequences not just for those who work with it, but also for those who live in its vicinity.
Due to a lack of understanding about E-Waste, it is difficult to manage it. As a result, a comprehensive recycling process must be implemented to protect us and future generations.
GOVERNMENT BODIES INVOLVED IN E-WASTE MANAGEMENT AUTHORIZATION:
- Central Pollution Control Board
- Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology
- State Board Pollution Board
E- WASTE RECYCLING BUSINESS
E-waste is well well-known source across the world even it poses major environmental threat. However, it allows a businessman to have their own e-waste recycling business. India creates major opportunities for the e-waste management business. For achieving success in this plan to develop the right e-waste recycling business plan is a crucial thing, which includes various phases in terms of processes like gathering devices, processing scrap & and receiving return payment for the components.
Every recycler shall ensure that the facility and recycling processes are in accordance with the standards as under the E-waste management and handling rule 2016 and guidelines prescribed by the Central Pollution Control Board from time to time.
Responsibility of Recycler:
- Obtain authorization from the concerned State Pollution Control Board in accordance with the procedure outlined in sub-rule (3) of rule 13;
- Ensure that no environmental damage occurs during the storage and transportation of e-waste;
- Ensure that the recycling processes have no negative impact on human health or the environment; and
- Make all records available for inspection to the Central Pollution Control Board or the concerned State Pollution Control Board.
- Ensure that fractions or materials not recycled in its facility are sent to the appropriate authorised recyclers;
- Ensure that residue generated during the recycling process is disposed of in an authorised treatment storage disposal facility;
- Maintain a Form-2 record of e-waste collected, dismantled, recycled, and sent to an authorized recycler and make this record available for inspection.
- On or before the 30th day of June following the financial year to which the return applies, file yearly returns in Form-3 with the appropriate State Pollution Control Board.
- Operation without Authorisation by any recycler, as defined in this rule, shall be considered as causing damage to the environment;
- may accept waste electrical and electronic equipment or components not listed in Schedule I for recycling, provided that they do not contain any radioactive material and that the same is indicated while taking the authorisation from the concerned State Pollution Control Board;
E-WASTE RECYCLING PROCESS:
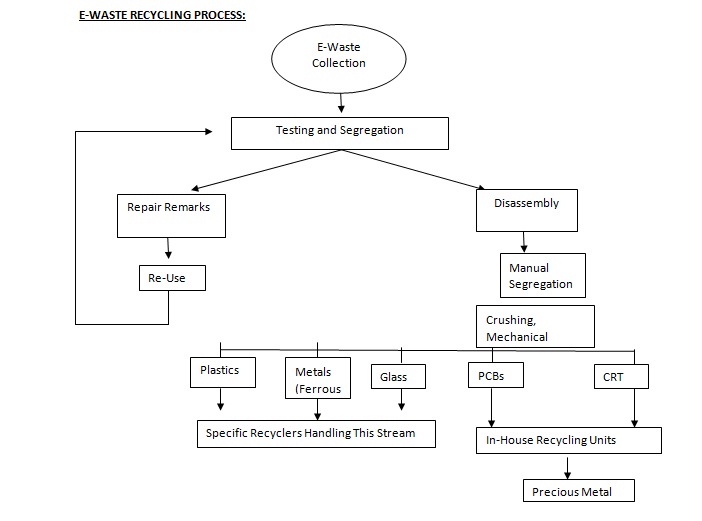
This process is highly labor-intensive, involving several people working together by following many steps, which are mentioned below:
- Sorting
- Dismantling
- Large size reduction process
- Small size reduction process
- Magnetic separation
- Metallic & non-metallic components separation
GOVERNMENT SUBSIDY FOR E-WASTE RECYCLING PLANS:
Is there any subsidy for an e-waste recycling startup in India? Yes, there is a recycling project. The subsidy is from both the central government as well as state government. The CG gives a subsidy of 25% or equivalent to the state subsidy, whichever is lower
BUSINESS MODEL: FOR E-WASTE RECYCLING BUSINESS
To decide the operational area of your e-waste recycling business based on your investment potential is a very critical task. On the other side, collecting scrap from direct consumers yields higher returns in terms of profit margin & also increases the brand recognition of your business.
SPACE REQUIREMENT FOR SETTING UP RECYCLERS:
A recycling plant with a capacity of 1 ton/day requires a minimum area of 500 square meters, and with a capacity of 5MT/day requires 2500 square meters.
LICENSES & PERMISSIONS
A number of Government permissions & licenses are required to start an e-waste recycling business. The steps to follow for an e-waste recycling business are mentioned below:
- First step is to register for the Udyog Aadhaar MSME status to start an e-waste recycling business online.
- Next step is to go to the state PCB & ask for permissions to start business by submitting various statutory documents.
- The last step is to take necessary approvals from the Ministry of Environment for importing e-scrap as a part of e- e-waste business plan.
Recycler should obtain
Authorisation of Facilities Possessing Environmentally Sound Management Practice for Dismantling Or Recycling Of E-Waste
For Authorization
- Submit Form 4 in triplicate to the concerned pollution board
- Submit the details and documents as required for the authorization
Documents:
- Unit address proof
- Business in the form of a company, then COI
- Proprietor/Director/Partner KYC (Aadhar & PAN)
- CTE and CTO license
- Copy of agreement with collection centre
- Copy of Agreement with producer
- Details of storage for raw materials and recovered materials